Feb 27, 2023An allocation base is the basis on which cost accounting allocates overhead costs. Learn more about what it is, how it works, and how it is computed. … Using a cost allocation base enables organizations to identify areas where costs can be reduced or controlled more efficiently. … 5550 Tech Center Drive Colorado Springs, CO 80919. Finance
Types of Digital Marketing and How Digital Marketing Works
Jun 22, 2023The next step is to find an allocation base that drives the cost of each activity. Step 3. Identify the cost driver for each activity. … Figure 3.5 shows the allocation of overhead using the cost driver activity just presented and the overhead rates calculated in Figure 3.4. Notice that allocated overhead costs total $8,000,000.

Source Image: crewcost.com
Download Image
Jun 8, 2023June 8, 2023 Costing & pricing Table Of Contents Introduction Common Techniques for Allocating Manufacturing Overhead Expenses Considerations for Choosing the Right Allocation Technique Benefits of Accurate Manufacturing Overhead Allocation Challenges and Limitations of Overhead Allocation Techniques Best Practices for Overhead Allocation
Source Image: venngage.com
Download Image
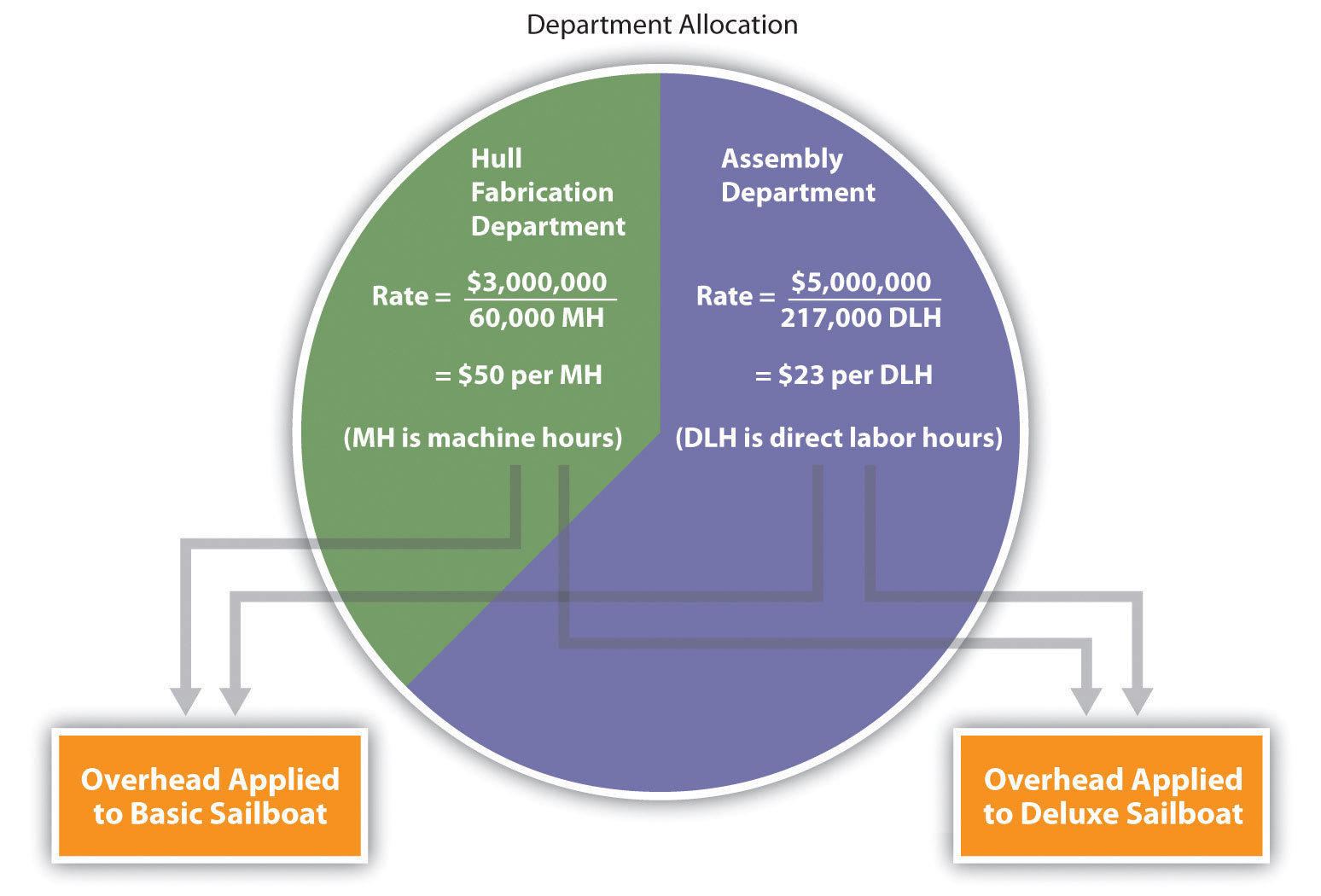
Virtual Call Assistant for Business Growth and Advantages Assembly department rate: $23 per direct labor hour (= $5,000,000 ÷ 217,000 hours) As shown in Figure 3.3 “Using Department Rates to Allocate SailRite Company’s Overhead“, products going through the Hull Fabrication department are charged $50 in overhead costs for each machine hour used.

Source Image: proprep.com
Download Image
Allocation Bases That Do Not Drive Overhead Costs
Assembly department rate: $23 per direct labor hour (= $5,000,000 ÷ 217,000 hours) As shown in Figure 3.3 “Using Department Rates to Allocate SailRite Company’s Overhead“, products going through the Hull Fabrication department are charged $50 in overhead costs for each machine hour used. Here are just a few options contractors might use as a basis for allocating overhead: total direct job costs. direct labor costs. direct labor hours. equipment costs. Selecting a basis for indirect cost allocation should make sense for the type of cost and for your type of business.
What are allocation bases that do not drive overhead costs?
Sep 11, 2023Overhead allocation is a process used in cost accounting to assign indirect costs to cost objects, such as products or departments. These indirect costs, also known as overhead costs, include expenses that are not directly tied to a specific product or service but are important for the overall operation of the business. Ecommerce Fulfillment: 3 Strategies To Fulfill Online Orders | BigCommerce

Source Image: bigcommerce.com
Download Image
32 Best Marketing Tactics to Drive More Sales Sep 11, 2023Overhead allocation is a process used in cost accounting to assign indirect costs to cost objects, such as products or departments. These indirect costs, also known as overhead costs, include expenses that are not directly tied to a specific product or service but are important for the overall operation of the business.

Source Image: shopify.com
Download Image
Types of Digital Marketing and How Digital Marketing Works Feb 27, 2023An allocation base is the basis on which cost accounting allocates overhead costs. Learn more about what it is, how it works, and how it is computed. … Using a cost allocation base enables organizations to identify areas where costs can be reduced or controlled more efficiently. … 5550 Tech Center Drive Colorado Springs, CO 80919. Finance
Source Image: bluehost.com
Download Image
Virtual Call Assistant for Business Growth and Advantages Jun 8, 2023June 8, 2023 Costing & pricing Table Of Contents Introduction Common Techniques for Allocating Manufacturing Overhead Expenses Considerations for Choosing the Right Allocation Technique Benefits of Accurate Manufacturing Overhead Allocation Challenges and Limitations of Overhead Allocation Techniques Best Practices for Overhead Allocation

Source Image: ossisto.com
Download Image
Overhead Allocation Smoothing Method Overhead costs are charged to the expense account, and they must be continually paid regardless of whether the company is selling goods or not. Some common examples of overhead costs are rental expenses, utilities, insurance, postage and printing, administrative and legal expenses, and research and development costs. Cost Allocation Mechanism

Source Image: builder-resources.com
Download Image
How Does an Organization Use Activity-Based Costing to Allocate Overhead Costs? Assembly department rate: $23 per direct labor hour (= $5,000,000 ÷ 217,000 hours) As shown in Figure 3.3 “Using Department Rates to Allocate SailRite Company’s Overhead“, products going through the Hull Fabrication department are charged $50 in overhead costs for each machine hour used.
Source Image: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Download Image
Overhead allocation: Allocating Overhead Costs to Control Cost of Goods Sold – FasterCapital Here are just a few options contractors might use as a basis for allocating overhead: total direct job costs. direct labor costs. direct labor hours. equipment costs. Selecting a basis for indirect cost allocation should make sense for the type of cost and for your type of business.

Source Image: fastercapital.com
Download Image
32 Best Marketing Tactics to Drive More Sales
Overhead allocation: Allocating Overhead Costs to Control Cost of Goods Sold – FasterCapital Jun 22, 2023The next step is to find an allocation base that drives the cost of each activity. Step 3. Identify the cost driver for each activity. … Figure 3.5 shows the allocation of overhead using the cost driver activity just presented and the overhead rates calculated in Figure 3.4. Notice that allocated overhead costs total $8,000,000.
Virtual Call Assistant for Business Growth and Advantages How Does an Organization Use Activity-Based Costing to Allocate Overhead Costs? Overhead costs are charged to the expense account, and they must be continually paid regardless of whether the company is selling goods or not. Some common examples of overhead costs are rental expenses, utilities, insurance, postage and printing, administrative and legal expenses, and research and development costs. Cost Allocation Mechanism